GPR Applications
Some application areas for GPR surveys and tasks:
- Geotechnical engineering, cable routing, pipeline inspection and routing, tunnel lining, location of buried utilities
- Cavities, old wells and voids detection
- Defectoscopy, bridge monitoring, road pavement inspection, railway bed inspection
- Profiling of walls, floors, ceilings, concrete structure inspection, location of rebars, concrete structure inspection
- Searching for different metallic and non-metallic objects (local items, pipes, wires, underground tanks etc.), buried into ground,
- Archaeology,
- Bedrock depth determination
- Mining development and machine guidance
- Mineral exploration, mine planning
- Water table determination
- Ground wastes investigations, environmental studies
- Industrial wastes deposits mapping
- Paleobed river detection
- River or lakes bottom profiling, hydrogeology
- Mapping of melted zones in permafrost
- Glaciology
- Forensic and medicine
- Other similar tasks
Archeology
Non - visible ancient building structures are detected when they are buried under one meter or dirt filling.
Much more efficient digging can be planed.
Laying a pipe or cable in a trench.
The kind of equipment and the method selected to bury a pipe/cable in a trench depends upon the ground characteristics:
Analysis of GPR imaging provides this kind of information prior digging the trench.
Road management and pavement survey.
A continues GPR data is recorded at high speed. The processed image shows the different pavement layers their thickness and the nature of the interfaces.
Rehabilitation of old industrial sites.
GPR mapping provides detection of buried waste materials such drums etc.
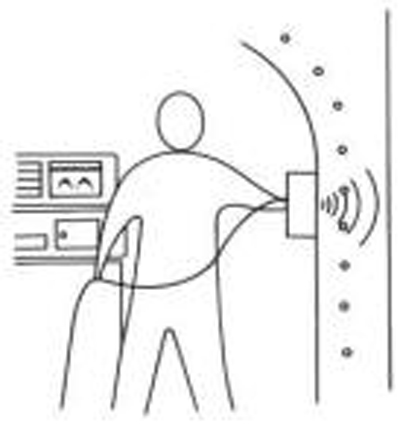
Rebar detection in a concrete structure.
A GPR grid recorded on the concrete wall provides an accurate image of inner rebars location.
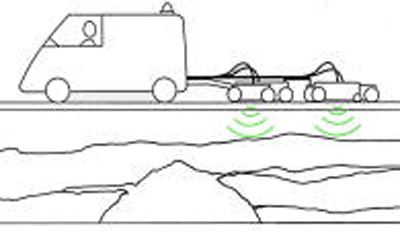
Road maintenance: preventing pavement collapse.
A GPR profile along the road shows previous substratum and potential pavement sinking above heterogeneous areas.
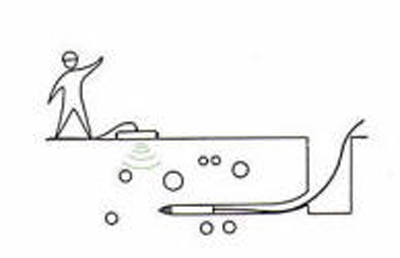
No-dig: laying out pipes and cables with horizontal drilling.
Detection of hard spots or buried obstacles ahead of the drilling tool.
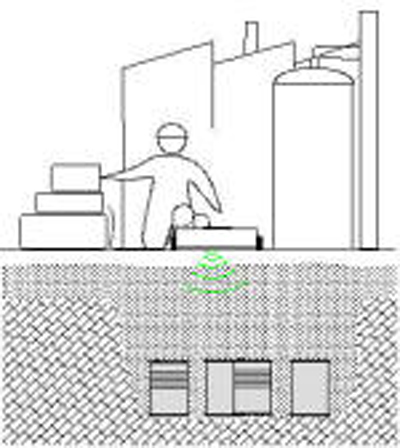
Utilities detection.
The GPR imaging locates the utility networks and other buried structures prior designing new underground work, including laying out of new utilities.
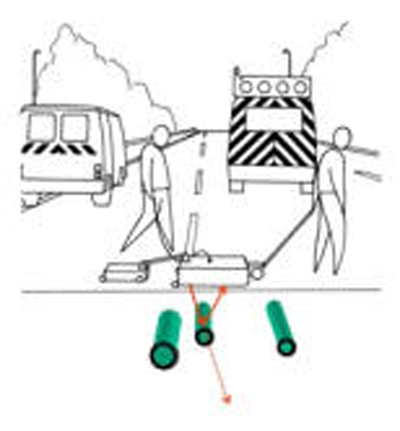
Detection of cavities under pavement.
The GPR images show potentially very dangerous cavities: location is confirmed by drilling prior adequate consolidation of the area.
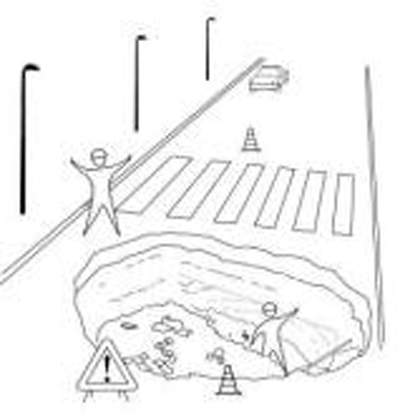
Critical analysis of old or recent structures.
Rebars are detected and actual thickness of the concrete sampled along the profile as a cracks in the structure.
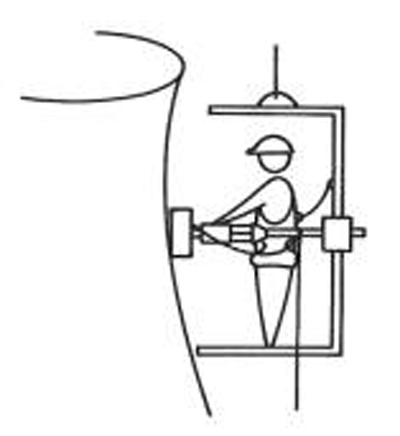
Sounding of a structure under coating.
Analysis of non visible structure defaults, hidden behind coating. Imaging the structure components and their interface.
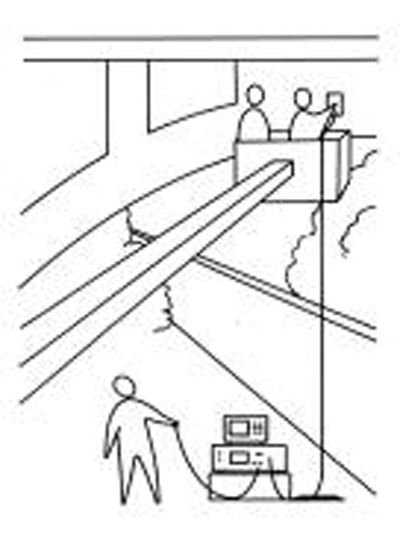
Checking of structure after rehabilitation.
The GPR imaging conducted prior and after injection shows the effects of the rehabilitation. Discrimination between zones where injection has been done or omitted.